H+O: Unified Egocentric Recognition and 3D Hand-Object Poses and Interactions
This paper proposes an end-to-end neural network architecture capable of jointly identifying 3D object and hand poses, and at the same time predicting the object and activity category for a RGB image in a single pass. The authors propose a novel representation method for jointly learning the 3D hand and object poses, and object and action categories. They also propose an interaction RNN for learning the interaction between 3D hand and object along the temporal dimension.
Methodology
The goal here is to understand human activities by interpreting the scenes in an egocentric video.
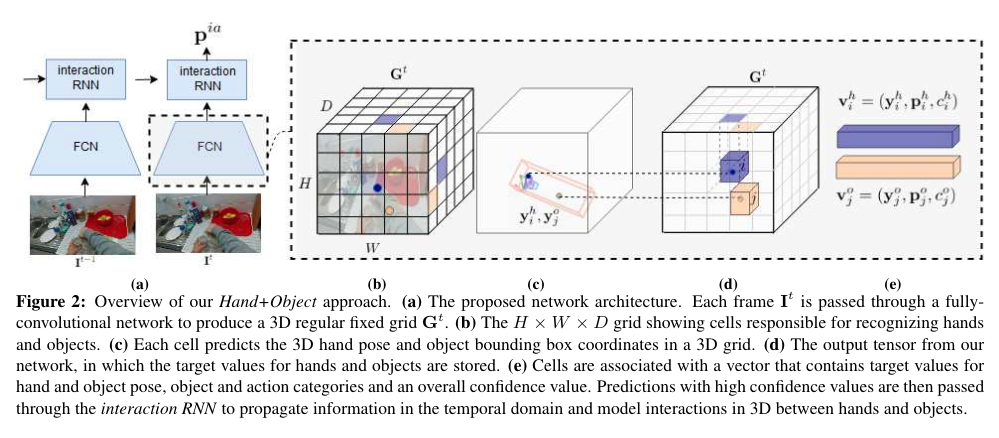
The model above takes in a sequence of images and predicts per-frame 3D hand and object poses, object and action categories, and per-sequences interaction classes. Hand and objects are represented as 3D control points. The input image is processed by a fully convolutional network and is divided into a regular grid containing cells. This grid spans the 3D scene in front of the camera. The target values for the hand and object at a specific cell location is stored in this grid as a multi-dimensional vector. In order to equally represent both hand and object each cell stores two sets of values. This helps in modeling the cases when hand/object is occluded by object/hand.
For modeling the interaction between hands and objects across the temporal domain, the authors add a recurrent module to integrate information across the frames. This module generates the probability scores over all the interaction classes.
Joint 3D Hand-Object Pose Estimation
The authors propose to use a common representation for both hand and objects, they use 21 3D control points for both hands and objects. The image is divided into a grid and depth is also made discrete. This divides the image into cells as shown in the figure above. As the control points are on 3D bounding boxes, computing 6D object pose becomes very easy. This eliminate the need to solve for 2D-to-3D correspondence problem and also helps in reducing the depth ambiguities. Hence, it helps in improving the object pose estimation accuracy. The network is also trained to predict high confidence values for the cells where the object/hand is present. Additional confidence value for the depth dimension is also calculated and weighted summation is performed for calculating the final confidence score. (See Section 3.2 in the paper for the formulas.)
Object and Action Recognition
The idea here is, the features learned for predicting the pose of hand and object should help in predicting the object and action classes. So, the authors store the vectors for object and action classes in the representation vectors for object and action, respectively. This equips the network to predict the 3D hand and object pose, action and interaction classes on a single pass of the image.
Temporal Reasoning and Interaction Modeling
The authors add the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) module to the architecture for reasoning along the temporal dimension. Instead of directly feeding the hand and object poses as an input to the temporal module, the authors model the dependencies between hands and object with a learned function. The resulting mapping is given as an input to the RNN. They call this as the interaction RNN.
Training
As it is difficult to keep all the activations of the sequences of images in the memory, the authors find it effective to train the network in two stages. First stage trains the network for predicting 3D hand and object poses, object and action categories. Second stage fixes the initial model and trains the recurrent network for propagating the information in the temporal domain.
Experiments and Conclusions
The authors evaluate the proposed methods on: First-Person Hand Action (FPHA), a portion of EgoDexter hand pose estimation dataset (they themselves annotated this portion of the data for 6D object pose), SynthHands 3D hand pose estimation dataset (for training).
Major conclusions/observations:
- The proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance on the task of egocentric activities recognition and 3D hand-object interactions.
- Interaction RNN performs much better than a standard RNN. The authors show that this module gives more importance to the fingers which interact commonly with the object.
- Predicting control points in 3D improves on the task of 6D object pose prediction.
- Having a joint representation for hands and objects helps in improving the combined pose estimation accuracy.
- The proposed approach generalizes well to the unconstrained environments and even perform well on the synthetic dataset.
- The method proposed is able to run in real-time at a speed of 25 fps on an NVIDIA Tesla M40.